Design flow

This document is in slide mode. t to toggle h for help
$^*$There are plenty of good books on Engineering design see[pahl96:_engin_desig_system_approac][pugh90:_total_desig][petroski06:_success][Ashby16:Materials_in_design][ashby13:_Materialsonline][haik2015engineering]
Engineering is the art of modelling materials we do not wholly understand into shapes we cannot precisely analyse, so as to withstand forces we cannot properly assess, in such a way that the public has no reason to suspect the extent of our ignorance.
Dr A.R. Dykes of the British Institute of Structural Engineers, (in 1976)
| - Creativity? | - Art? |
| - Compromise? | - Ideas? |
| - Communication? | - Solutions? |
| - Aesthetics? | - Business? |

Each component may require a dialog with other designers, experts, 'sales force/customers'\footnote{i.e. who wants the design and for what}
What might be the best way to design something - Where do we start?
As a design process progresses the solution or product becomes more obvious. This does not imply that there is a linear flow from concept to product!
As the designer or design group learns more and more about the problems and solutions she/he/they may decide to go back earlier stages to make sure that the eventual project will work! Likewise we may want to find a suitable manufacture in early stages so he or she can help with some of the problems.
This first stage is needed to clarify what is needed.
This may seem a trivial task but it is the most important stage of a design. We may need to restate parts of the problem as we go through the design but if this first phase will become a yard stick by which we measure success.
`What is the best way to cut the grass', is not a good way to state the problem. `What is the best way to keep the lawn in short' is better since this does not assume the answer is a lawn mower. Artificial turf, chemicals or a flock of sheep may all be good ways to keep up appearances!
The purpose of the Product Specification stage is to define the requirements for the final product. This provides a a clear foundation on which a product may be designed. We need to outline what the product should do, but we also need to identify whatever limitations we may for see. We need to determine attributes such as a likely power source, what it should be made of, how heavy it can be and how long it should last. All this information must eventually make its way onto a Product Design Specification sheet (or PDS).
Suppose we needed to come up with a way to move around easily this could result in a bicycle, an automobile, an aeroplane, a wheelchair, a skate board, or a train. However on further consideration of the problem we may outline the need for a machine that is
A wheel chair would be a possible solution.
Suppose we needed to come up with a way to record meetings, we could use a phone voice recorder, pencil and paper, or a phone video/camera. However on further consideration of the problem we may outline the need for a machine that is
A pencil and paper would be the ideal solution. If the pencils hadn't been invented the design group would go to the next step!
\begin{tabular}[h]{ll} \multicolumn{2}{c}{Some design attributes to consider}\\\hline performance& how fast\\ how slow& how often\\ tolerances& environment\\ temperature range& pressure range\\ humidity& noise level\\ life in service& maintenance\\ cost& size\\ weight& aesthetics\\ materials, standards& ergonomics\\ quality& reliability, testing\\ safety, market, quantity& liability patents\\ installation& documentation \end{tabular}
This is the part of the design process where anything goes. Look at what similar products do, are there any ideas we can copy from nature, see how do other people solve the problem - why didn't it work!,
The purpose of the conceptual design stage is to use the design specification to invent new device. As many new devices as possible are invented and discussed with the design group but they should all be workable solutions to the guidelines of the design specification. This is the point where you can champion your favourite idea, it may not be the one that works but it encourages you and others in the design group to generate even more new and creative ideas and inventions. The human interface is a vital part of the design and particular emphasis should be placed on this. The first prototypes for the new idea may emerge at this stage. At last something that can actually be seen and played with!
This is a useful method to evaluate and make design decisions. The idea can also be applied to evaluating components, products, leaders etc.
Since several variations of a solution should result from the ideas generated by the design team, the group will need to consider each in turn several times until a solution concept emerges. The solution concept is a more concrete description of the form and structure of the device that meets the specifications of the design specification. Two important points should be highlighted regarding the creative process of humans:
| Solution variant | Fast | CO2 emissions | Cost | Ambient Noise | Running cost |
 | |||||
 | |||||
 |
A similar table could be used to decide which mobile phone to buy
| Phone type | Model | G5 (y/n) | cost | weight | My rating |
| Android | |||||
| iPhone |
Once a concept has been established and shown to be the best There may be multiple solutions and no clear best solution, after all there are many many different designs of television set, automobiles... Better mousetraps may still be needed!
Table of Costs associated with design changes at each stage of the design Detail Design. The purpose of the Detailed Design stage is to produce a complete description of the product or device described by the Solution Concept. Although some of this detail may already have been formulated as part of the Conceptual Design stage, in the Detailed Design stage, the Solution Concept must be completely specified. A detailed specification includes:
that are being purchased.
Prototype Construction .. at last something that works! it is desired that the usefulness of a particular product or device be evaluated. In order to carry out such an evaluation, a prototype of the device will be constructed and a suitable set of trials will be performed. The results of these trials will be used to evaluate the product and to determine if any re-design must be carried out or if the device is suitable to be manufactured or published. At this stage, marketing approaches will be determined by any manufacturers who have agreed to produce the prototype.
Strength relates to shape and material
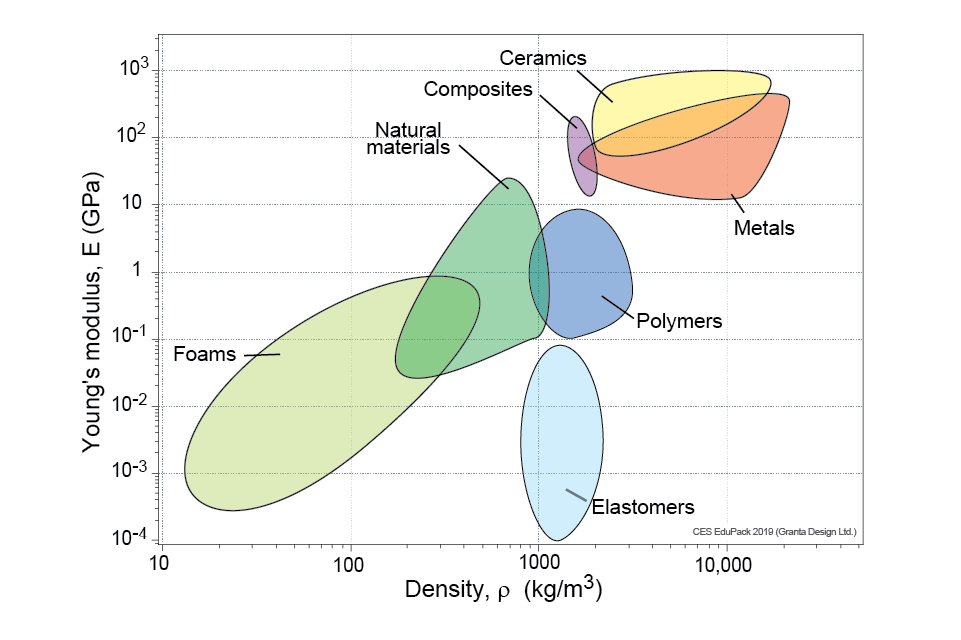
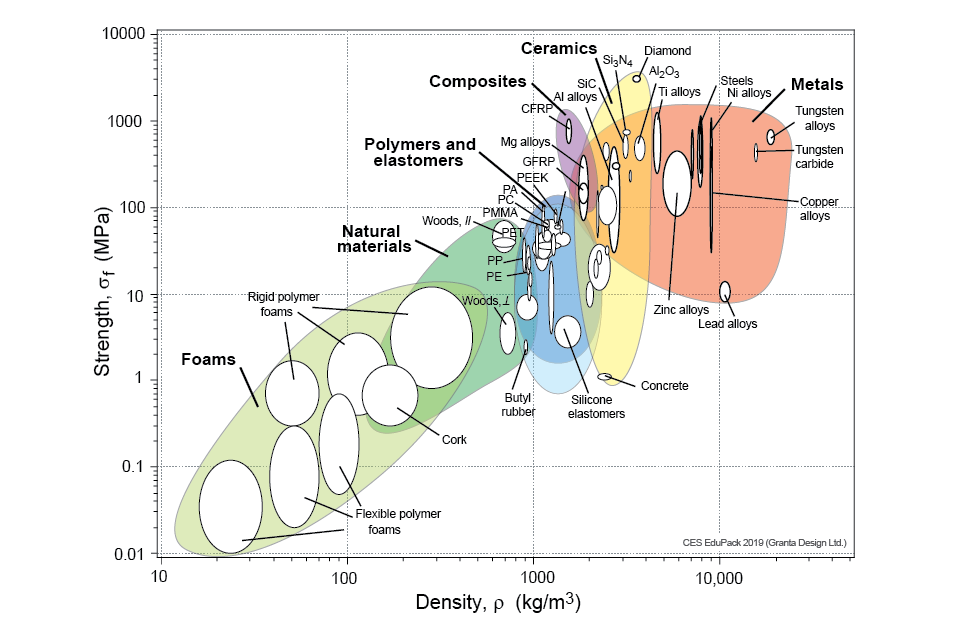
see (https://www.grantadesign.com/education/students/charts/)
slide: